📋 The uname command in Termux provides information about the system, unveiling details about the machine and its operating system. 🖥️
uname
To obtain basic system information, use the ‘uname‘ , Retrieve system information with the below command in termux.
uname 
Gain insights into your system’s architecture and kernel version using the “uname” command, as illustrated in the example above. 🌐
Additional Options : 🛠️
The “uname” command offers additional options to retrieve specific system information
uname -a This command provides detailed information about the system, including the machine architecture and kernel version. 🌟
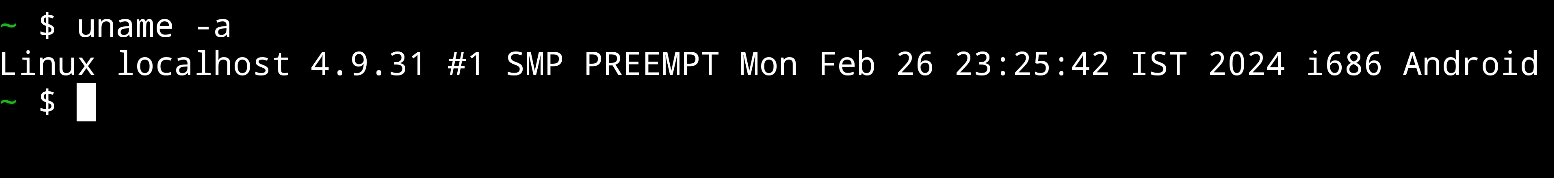
For a concise display of the system’s architecture, use the following command: 📋
uname -m These additional options enhance the versatility of the “uname” command for comprehensive system information. 🌐

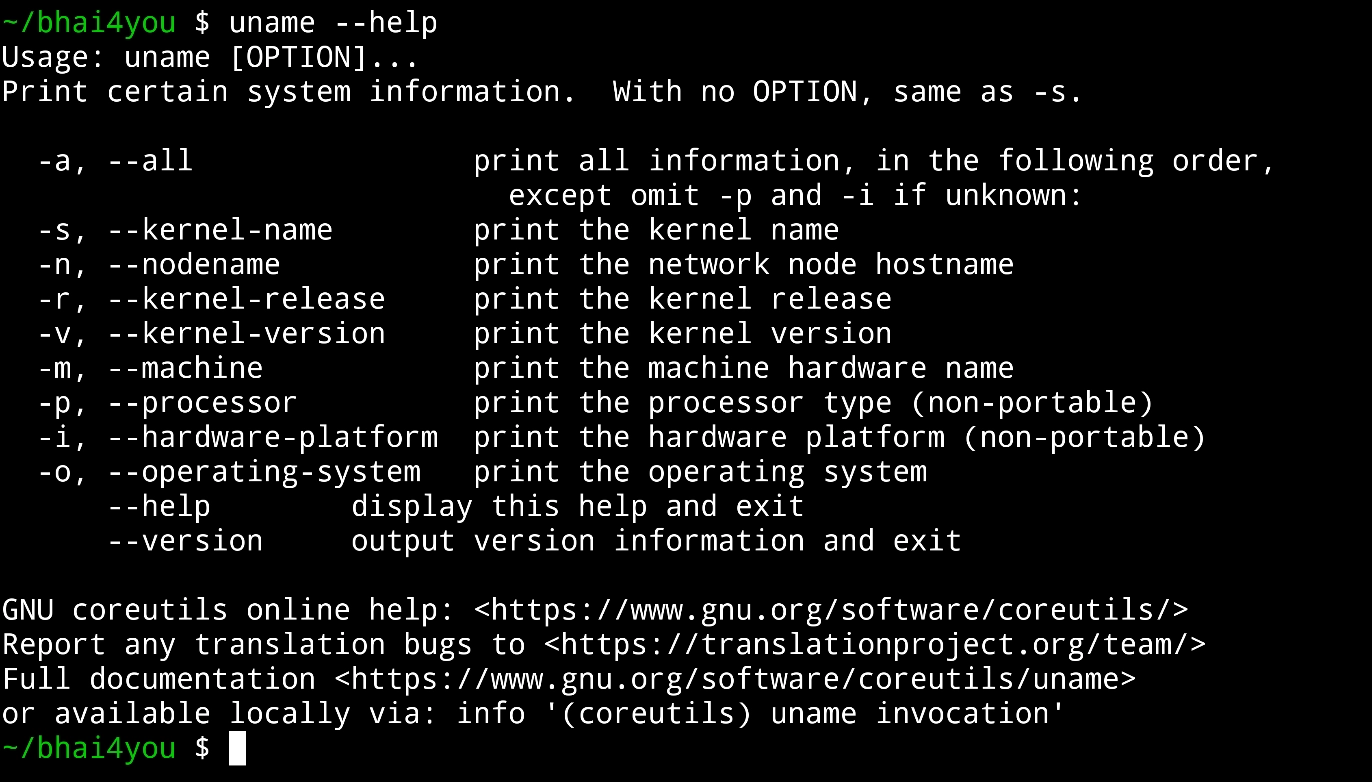
For additional options and information about the “uname” command, you can use the “–help” flag. Running the following command:
uname –help
uname --helpThe “–help” flag provides detailed information about the usage and options of the “uname” command, allowing you to explore its functionalities further. 💡
The “uname” command in Termux is a versatile tool for managing and exploring system-related information, making it an essential component of your command-line toolkit. 🖥️🌟