Introduction to Internet
Table of Contents :
What is Internet ?

The internet is like a gigantic global playground where you can play games, talk to friends, and learn new things!, send messages, share pictures, and find information about anything you’re curious about. Just like how you use roads to get to different places, the internet has “cyber roads” that help you travel from one website to another. 🚗💨
It’s a magical network of computers around the world connected to each other.
So, the internet is like a fun and exciting world where you can discover, play, and connect with others!
Why is the Internet Called a Network? 🤔
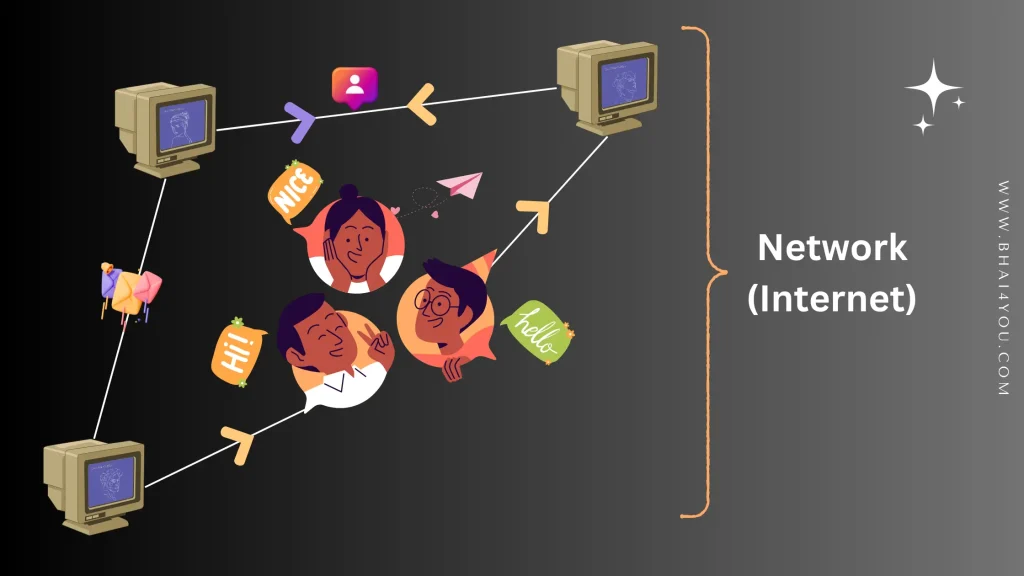
The internet is called a network because it’s made up of a vast number of interconnected computers and devices.
Just like how roads connect cities, the internet connects computers, creating a network that spans the entire globe.
just Imagine lots of computers sitting around, all over the world. Each computer is like a friend in a big room. now lines connecting these computers, like strings connecting balloons. These lines are how the computers talk to each other. When all these computers are connected, working together, and chatting with each other through these lines, you’ve created a network. Just like friends talking and sharing things.
We call this big, worldwide network the “Internet” It’s like a super-duper network because it connects millions and millions of computers all around the globe.
How Does the Internet Work?🕸️

At its core, the internet relies on a set of rules and protocols, like the TCP/IP protocol suite, which enables seamless communication between devices. Data is broken into packets, which travel through the network, reaching their destination where they’re reassembled.
Think of it like sending letters that are broken into pieces and then put back together upon arrival.
What is Different Between WWW and Internet ?

The internet is the infrastructure, while the World Wide Web (WWW) is a way to access information on the internet. Think of the internet as the entire library and the WWW as the books and shelves within that library.
History of the Internet ?📜
The internet’s roots trace back to the 1960s, initially developed for military and research purposes. Over time, it evolved into a global phenomenon, with the World Wide Web becoming publicly accessible in the early 1990s.
Advantage & Disadvantage
Advantages of the Internet 👍
- Information Access: A wealth of knowledge at your fingertips.
- Communication: Instant connection with people globally.
- Entertainment: Endless options for music, videos, and games.
- Business Opportunities: E-commerce and global market reach.
Disadvantages of the Internet 🚫
- Cybersecurity Threats: Hacking, phishing, and other malicious activities.
- Information Overload: Too much information can be overwhelming.
- Privacy Concerns: Personal information may be at risk.
- Addiction: Excessive internet use can lead to addiction.
How do I Connect to the Internet ?📡
- Wi-Fi: Wireless connection using a router.
- Broadband : Through cable or DSL connections.
- Mobile Data: Using cellular networks.
- Satellite: Via satellite signals in remote areas.
Types of Internet Service 🌐
DSL provides internet access through telephone lines. It operates on a frequency that allows simultaneous internet use and phone calls. Speeds can vary based on the distance from the provider’s central office.
Example : AT&T DSL, Verizon DSL
Cable internet uses the same coaxial cables as cable television. It offers high-speed internet, with download speeds often higher than upload speeds. It’s popular in urban areas where cable infrastructure is well-established.
Example : Comcast Xfinity, Spectrum
Fiber optic cables transmit data using light signals, providing exceptionally fast and reliable internet. Fiber is known for low latency and high bandwidth, making it suitable for demanding online activities.
Example : Verizon Fios, Google Fiber
Satellite internet beams signals to and from satellites, offering coverage in remote areas. It’s a solution for users without access to traditional wired services, though it can have higher latency.
Example : HughesNet, Viasat
Wireless internet enables devices to connect without physical cables, commonly through Wi-Fi routers. It’s prevalent in homes, offices, and public spaces, allowing flexibility in device mobility.
Example : Linksys, Netgear
Mobile broadband uses cellular networks for internet access. It’s widely used with smartphones, tablets, and portable hotspots, providing on-the-go connectivity.
Example : Jio, Airtel, Vodaphone, Verizon Wireless, T-Mobile
Dial-up uses telephone lines to connect to the internet, but it’s an older and slower technology. It ties up the phone line during use and has largely been replaced by faster options.
Example : AOL (historically)
Fixed wireless transmits internet signals from fixed points via radio waves. It’s commonly used in rural areas where laying cables is impractical, providing an alternative to wired services.
Example : Rise Broadband, Nextlink
History and Evolution of Internet 🔄
- 1960s: ARPANET, the precursor to the internet, developed.
- 1970s: Email and TCP/IP protocol introduced.
- 1980s: Domain Name System (DNS) established.
- 1990s: World Wide Web became publicly accessible.
- 2000s: Rise of broadband and social media.
- 2010s: Mobile internet and the Internet of Things (IoT) gained prominence.
That’s it i hope you enjoyed this post and understand what is internet and how it works ! if you have any questions feel free to ask in comment section.
thanks for reading ♥